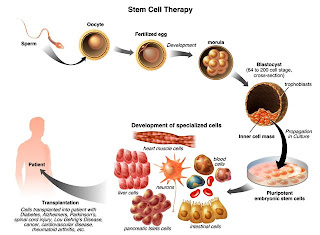
Most cells in our body have a specific function in particular
organs, such as the liver, skin or brain. The stems cells have a unique
potential of regenerating and developing into different types of cell in the
body during early age thus enabling treatments for diseases and
injuries, many of which cannot be treated with traditional medical methods. Stem
cells are non toxic and devoid of side effects compared to its toxic drug counterparts.
The use of stem cells for therapeutic purposes can ensure lower treatment costs
and promote longer lives. Stem Cells are the building blocks of our body. They have the
unique capability of replacing damaged cells and tissues and repairing the
damage cause to the body.
What is stem cell medicine?
Stem Cells hold the potential to cure
many diseases. Stem Cells are the fountainhead of all mature cells in the body.
They retain the ability to self-renew and differentiate into a variety of
different tissues. Recent studies show that Stem Cells are not restricted to
one lineage, but can differentiate along different lineages when placed in the
appropriate micro-environment, thus potentially opening up new vistas
especially in the field of regenerative medicine.
More
than 45,000 people across the world are receiving Stem Cell transplant every
year. Stem Cell technology can reduce pharmaceutical R&D by 25% each year,
with savings of up to US $25 million in each drug market. The first successful
stem cell transplant was conducted in 1988 for Fanconi’s anemia and since then
research in this field has grown by leaps and bounds.
Stem
cell therapy consists of introduction of highly potential stem cells into the
blood stream or the damaged tissues of the patient. The ability of stem
cells to self-renew offers a large potential to repair/replace damaged tissues
in the body. Given their unique regenerative abilities, stem cells offer
hope to patients with terminal illness and various conditions and diseases that
cannot be adequately treated.